How do scientist classify living things?- The members of each group of living things share a set of special features unique to that group.For example, plants contain a chemical called chlorophyll that they use to make their own food (it also makes them green). Every member of the plant kingdom shares this characteristic.Scientists are always looking for these characteristics or 'observable features' which allow them to group different species together and see how they are related to each other.
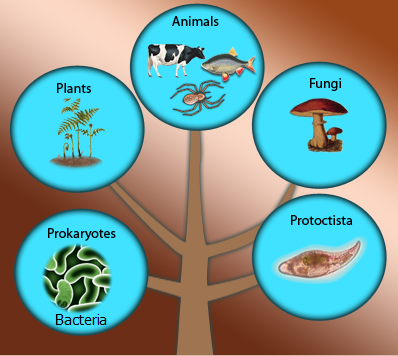
we are going to learn about the main four living things..
ANIMALS- PLANTS- microorganisms such as FUNGI AND BACTERIA
- ANIMAL KINGDOM
How do we divide the animal kingdom?
Taking the animal kingdom as an example, we can see that it is split into two clear groups:
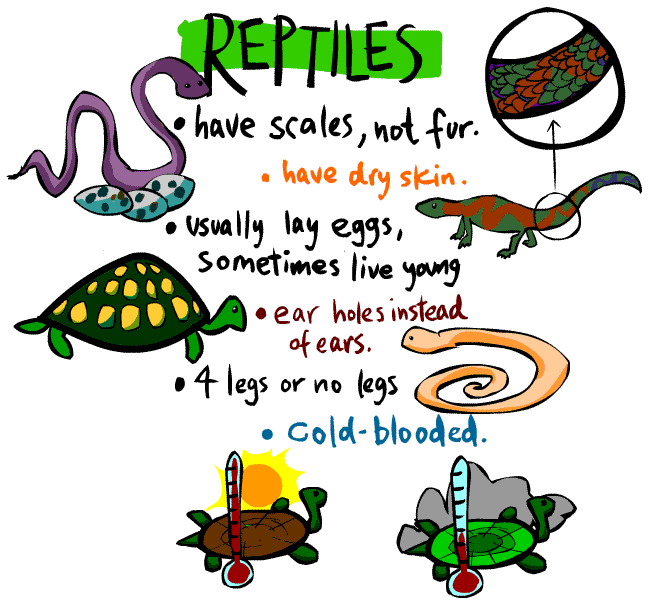
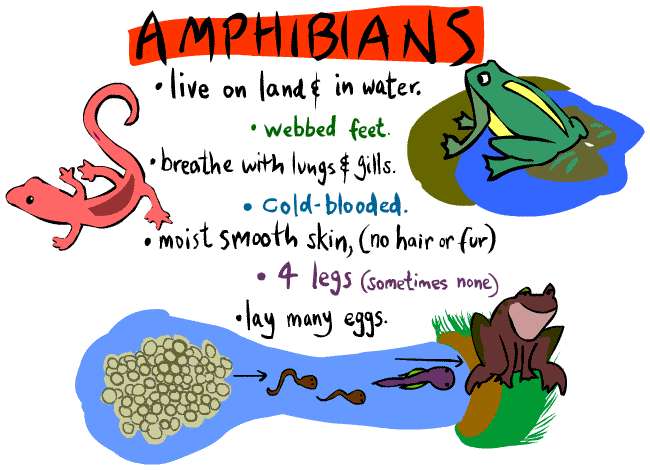
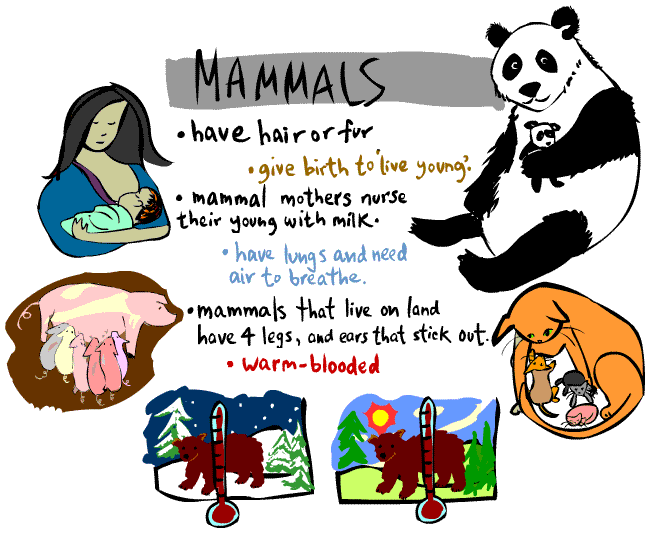
Invertebrates - animals without a backbone.
Vertebrates - animals with a backbone.
Vertebrates - animals with a backbone.
The animals have been divided into two groups based on the presence or absence of a backbone. The backbone is the observable feature that defines whether the animal is a vertebrate or an invertebrate.
These groups are divided into smaller 'sub-groups'.
Sponges, corals, worms, insects, spiders and crabs are all sub-groups of the invertebrate group - they do not have a backbone.
Fish, reptiles, birds, amphibians and mammals are different sub-groups of vertebrates - they all have internal skeletons and backbones.
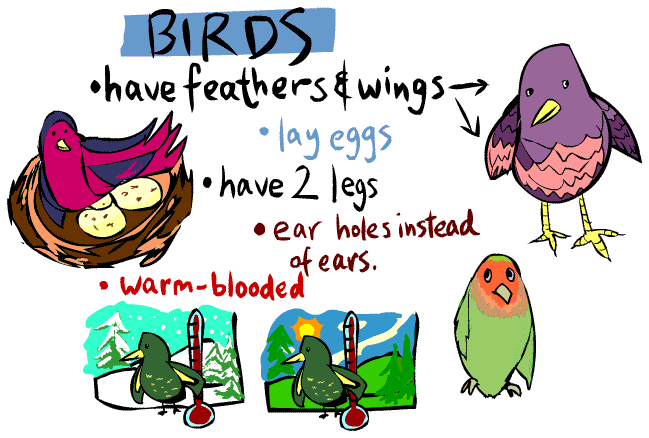
The animals that belong to these sub-groups all share the observable features of that group. Just as all the vertebrates have backbones, all birds have feathers and lay eggs, and all mammals have fur and suckle their young.
To see find out more about the observable features of these sub-groups and to see how they all fit together you can have a look at the relationship 'tree' - or what we like to call The tree of life.
VERTEBRATE ANIMALS AND INVERTEBRATES ( ONLY INSECTS)

https://www.sheppardsoftware.com/content/animals/kidscorner/classification/kc_classification_fish.htm
plants
Flowering plants
Flowering plants are categorized as high-class plants. At the adult stage, the plant produces flowers which can develop into fruits and seeds after being pollinated and fertilized. Rose, hibiscus, sunflower, mango, mango, banana, and papaya are flowering plants.

Non- flowering plants
Non- flowering plants do not carry flowers they produce spores, fungi or cones the are used for propagation (reproduction). Algae, moss, fern and conifer are no flowering plants.
Examples of non-flowering plants

fungi
Fungi are a group of living organisms which are classified in their own kingdom. This means they are not animals, plants, or bacteria. Unlike bacteria, which have simple prokaryotic cells, fungi have complex eukaryotic cells like animals and plants. Fungi are found throughout the Earth including on land, in the water, in the air, and even in plants and animals. They vary widely in size from microscopically small to the largest organisms on Earth at several square miles large. There are more than 100,000 different identified species of fungi.
Roles of Fungi Food -
Roles of Fungi Food -
Many fungi are used as food such as mushrooms and truffles. Yeast, a type of fungi, is used when baking bread to help it rise and to ferment beverages. Decomposition - Fungi play an important role in the decomposition of organic matter. This decomposition is necessary for many of the cycles of life such as the carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen cycles. By breaking down organic matter, fungi release carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen into the soil and the atmosphere. Medicine - Some fungi are used to killed bacteria that can cause infections and disease in humans. They make antibiotics like penicillin and cephalosporin.
How are fungi different from plants?
How are fungi different from plants?
they are different from plants in two important ways: 1) fungi cell walls are composed of chitin rather than cellulose (plants) and 2) fungi do not make their own food like plants do through photosynthesis. Characteristics of Fungi They are eukaryotic. They get their food by decomposing matter or eating off their hosts as parasites. They do not possess chlorophyll like plants. They reproduce through numerous spores rather than pollen, fruit, or seeds. They are usually not motile, meaning they cannot actively move around.
Scientists often divide fungi into four groups: club fungi, molds, sac fungi, and imperfect fungi. Some of the more common fungi that you are likely to see or use everyday are described below. Mushrooms - Mushrooms are part of the club fungi group. Mushrooms are the fruiting body of a fungus. Some mushrooms are good to eat and are used as food, while others are very poisonous. Never eat a mushroom you find in the woods! Mold - Molds are formed by filaments called hyphae. Molds tend to form on old fruit, bread, and cheese. They sometimes look furry as the hyphae grow upward and release more mold spores from their tips. Yeast - Yeasts are small round single-celled organisms. Yeasts are important in making bread rise.
BACTERIA
What are bacteria?
Bacteria are tiny little organisms that are everywhere around us. We can't see them without a microscope because they are so small, but they are in the air, on our skin, in our bodies, in the ground, and all throughout nature. Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms. Their cell structure is unique in that they don't have a nucleus and most bacteria have cell walls similar to plant cells. They come in all sorts of shapes including rods, spirals, and spheres. Some bacteria can "swim" around using long tails called flagella. Others just hang out or glide along.
Are bacteria dangerous?
Most bacteria aren't dangerous, but some are and can make us sick. These bacteria are called pathogens. Pathogens can cause diseases in animals and plants. Some examples of pathogens are leprosy, food poisoning, pneumonia, tetanus, and typhoid fever. Fortunately, we have antibiotics we can take which help to fight off the bad pathogens. We also have antiseptics to help us keep wounds clean of bacteria and antibiotic soap we use to wash to help keep off bad pathogens. Remember to wash your hands!
Are bacteria all bad?
Not at all. Actually most bacteria are very helpful to us. They play an important role in the planet's ecosystem as well as in human survival.
http://www.ducksters.com/science/bacteria.php FOR MORE INFO...
http://easyscienceforkids.com/bacteria-good-guy-or-bad-guy/

No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario